Titanium alloys are high-performance materials renowned for their exceptional strength-to-weight ratio, outstanding corrosion resistance, and biocompatibility. These alloys are widely used in aerospace, medical implants, chemical processing, marine engineering, and high-performance automotive applications.
This document provides a detailed technical analysis of titanium alloys, covering:
✔ Chemical compositions of key grades
✔ Physical & mechanical properties (with comparison tables)
✔ Advantages over competing materials (steel, aluminum, nickel alloys)
✔ Industrial applications & cost-performance analysis
✔ High-performance uses in extreme environments
Overview of Titanium Alloys
Titanium alloys, renowned for their exceptional strength-to-weight ratio, corrosion resistance, and biocompatibility, are critical in high-performance industries such as aerospace, biomedical engineering, and marine applications. Developed since the 1950s, these alloys are classified into α, β, and α+β types based on their microstructural phases, each offering unique mechanical and thermal properties.
This report analyzes three primary titanium grades—Ti-6Al-4V (Grade 5), Ti-5Al-2.5Sn (Grade 6), and Ti-Beta 21S (Grade 19)—comparing their chemical compositions, physical/mechanical properties, advantages, applications, and cost considerations.
Chemical Composition of Titanium Alloys
| Alloy | Ti (%) | Al (%) | V (%) | Fe (%) | Mo (%) | Other Elements |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Grade 1 (CP Ti) | ≥99.5 | – | – | ≤0.20 | – | O, N, C, H |
| Grade 2 (CP Ti) | ≥99.2 | – | – | ≤0.30 | – | O, N, C, H |
| Grade 5 (Ti-6Al-4V) | 90 | 6 | 4 | ≤0.25 | – | O, N, C, H |
| Ti-6Al-2Sn-4Zr-2Mo | 86.5 | 6 | – | – | 2 | Sn (2%), Zr (4%) |
| Beta-C (Ti-3Al-8V-6Cr-4Zr-4Mo) | ~75 | 3 | 8 | – | 4 | Cr (6%), Zr (4%) |
Key Notes:
Grade 1 & 2: Commercially pure (CP) titanium, excellent corrosion resistance but lower strength.
Grade 5 (Ti-6Al-4V): Most widely used alloy (~50% of all titanium applications).
Beta alloys (e.g., Beta-C): High strength, heat-treatable, used in aerospace fasteners.


Physical Properties of Titanium Alloys
| Property | Grade 2 (CP Ti) | Ti-6Al-4V (Grade 5) | Stainless Steel 316 | Aluminum 7075 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Density (g/cm³) | 4.51 | 4.43 | 8.00 | 2.81 |
| Melting Point (°C) | 1668 | 1604-1660 | 1370-1400 | 477-635 |
| Thermal Conductivity (W/m·K) | 16.4 | 6.7 | 16.3 | 130 |
| Electrical Resistivity (μΩ·cm) | 55 | 170 | 74 | 53 |
Mechanical Properties of Titanium Alloys
| Property | Grade 2 (Annealed) | Ti-6Al-4V (Annealed) | Ti-6Al-4V (Aged) | Stainless 316 | Al 7075-T6 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tensile Strength (MPa) | 345-483 | 895-930 | 1170-1200 | 515-620 | 572 |
| Yield Strength (MPa) | 275-345 | 825-869 | 1100-1150 | 205-310 | 503 |
| Elongation (% in 50mm) | 20-25 | 10-15 | 8-10 | 40-50 | 11 |
| Hardness (Rockwell) | 80-90 HRB | 36 HRC | 38-42 HRC | 80-90 HRB | 79 HRB |
Key Advantages of Titanium Alloys:
✔ Highest strength-to-weight ratio among engineering metals.
✔ Superior corrosion resistance (seawater, chlorine, acids).
✔ Biocompatible (ideal for medical implants).
✔ High-temperature stability (up to 600°C for some alloys).
✔ Fatigue & crack resistance (critical in aerospace).
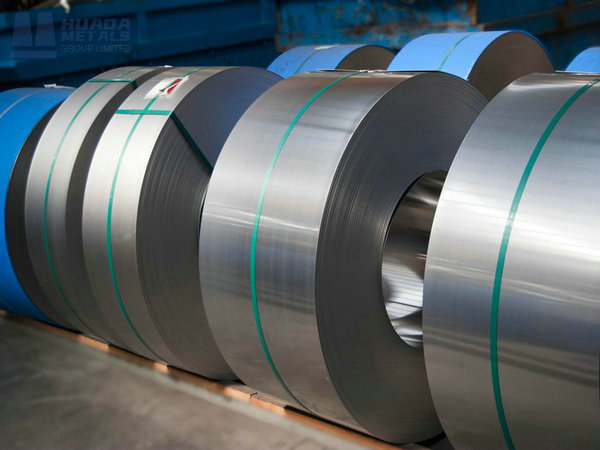
Available Product Forms
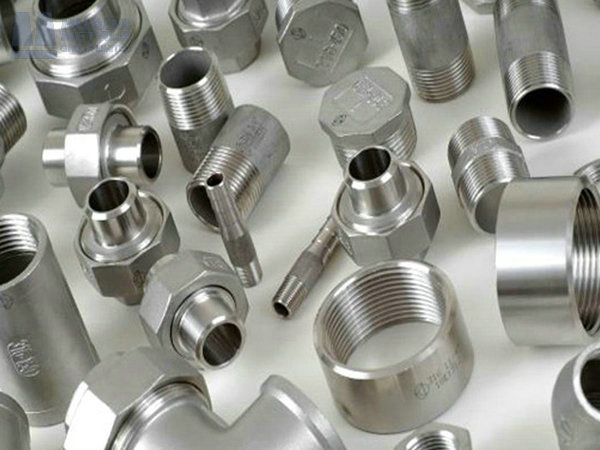
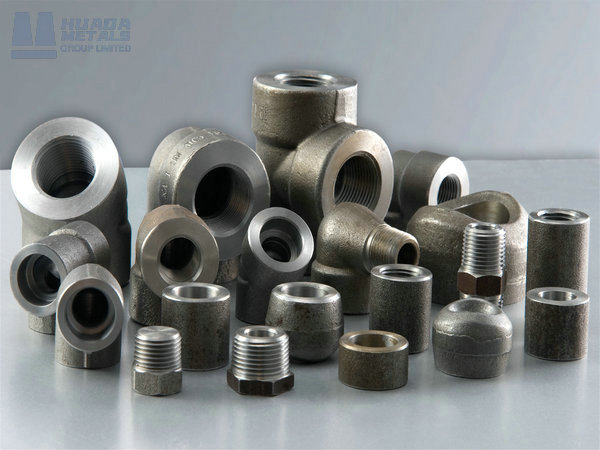





Quality Assurance
Key Properties and Advantages of Alloys
| Feature | Ti-6Al-4V (Grade 5) | Ti-5Al-2.5Sn (Grade 6) | Ti-Beta 21S (Grade 19) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Corrosion Resistance | Excellent in seawater, acids, and alkalis (passive oxide layer) | Similar to Grade 5, but better creep resistance | Superior in saline and chloride environments (Nb/Mo additions) |
| High-Temperature Strength | Maintains strength up to 400°C | Retains 70% strength at 550°C | Maintains strength up to 450°C |
| Machinability | Poor (work-hardens rapidly) | Moderate (better than Grade 5) | Improved (due to β-phase stabilization) |
| Weldability | Good (AWS ERTi-6Al-4V filler) | Fair (preheat required) | Excellent (low crack sensitivity) |
| Cryogenic Performance | Retains toughness at −253°C | Similar to Grade 5 | Superior toughness at −196°C |
| Biocompatibility | FDA-approved for implants | FDA-approved for implants | FDA-approved for implants (low oxygen content) |



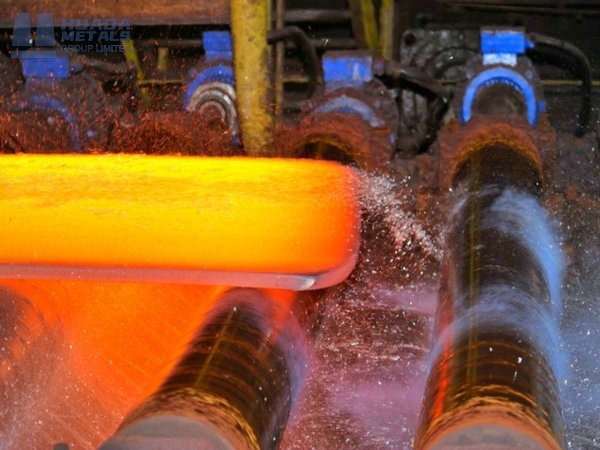
Manufacturing and Processing of Alloys
Applications of Alloys
Primary Industries Using Titanium Alloys:
Aerospace (aircraft frames, jet engines, landing gear)
Medical (implants, surgical instruments, dental screws)
Marine & Offshore (propeller shafts, subsea components)
Chemical Processing (heat exchangers, reactors, piping)
Automotive & Motorsports (high-performance exhausts, connecting rods)
Energy (nuclear reactors, geothermal drilling)
| Feature | Ti-6Al-4V (Grade 5) | Stainless Steel 316 | Aluminum 7075 | Inconel 718 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Strength-to-Weight | ★★★★★ (Best) | ★★ | ★★★★ | ★★★ |
| Corrosion Resistance | ★★★★★ (Seawater, acids) | ★★★★ (Pitting risk) | ★★ (Galvanic) | ★★★★★ (Extreme heat) |
| Cost (per kg) | $$$$ (~50−50−100) | $$ (~5−5−10) | ( ( 3-$5) | $$$$$ (~80−80−150) |
| Machinability | ★★ (Difficult) | ★★★★ (Good) | ★★★★★ (Easy) | ★ (Very hard) |


| Industry | Ti-6Al-4V (Grade 5) | Ti-5Al-2.5Sn (Grade 6) | Ti-Beta 21S (Grade 19) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Aerospace | Engine blades, landing gear, fasteners | Turbine disks, compressor blades | Wing structures, fuselage frames |
| Biomedical | Orthopedic implants (hip/knee joints) | Dental implants, bone screws | Spinal cages, trauma plates |
| Marine Engineering | Ship propellers, seawater piping | Subsea valve components | Desalination units, heat exchangers |
| Oil & Gas | Downhole tubing, wellhead components | Corrosion-resistant fittings | Subsea connectors, flowlines |
| Automotive | Lightweight suspension components | Exhaust manifolds | High-performance engine parts |
Cost & Performance Analysis
Grade 1 & 2 (CP Ti): Lower cost (~20−20−40/kg), used in chemical & marine applications.
Grade 5 (Ti-6Al-4V): Higher cost (~50−50−100/kg), dominant in aerospace & medical fields.
Beta Alloys (e.g., Beta-C): Premium price (~100−100−200/kg), used in specialized aerospace fasteners.
In Conclusion
Titanium alloys remain irreplaceable in industries demanding lightweight, corrosion-resistant, and high-strength materials. While Ti-6Al-4V dominates general-purpose applications, Ti-5Al-2.5Sn excels in high-temperature environments, and Ti-Beta 21S optimizes biocompatibility and marine corrosion resistance.
Future Trends:
- Additive manufacturing (3D printing) reduces waste in complex Ti-Beta 21S orthopedic implants.
- Grain boundary engineering may enhance fatigue resistance in Ti-6Al-4V for next-gen aerospace engines.
Titanium alloys offer unmatched performance in industries where lightweight strength, corrosion resistance, and reliability are critical. While the initial cost is higher than steel or aluminum, the long-term benefits (fuel efficiency in aerospace, longevity in implants, corrosion-free marine structures) justify the investment. HuaDa Metals has the good quality inconel alloys and contact us.
